About Windows (CMD) Command Prompt Commands Use Process
The command line of Windows can do extra
than you think
With current Windows versions, nearly the
entirety works at the click on of a mouse. But there is no other way to supply
instructions to a laptop - fragile however efficient: command line or enter on
the spot is aware of sturdy commands.
How to begin a command line:
You can name this specific mode from
Windows in a range of ways:
Right-click the Start button and choose the
Command Prompt option
The same menu, however solely with the aid of
keyboard: [Win + X] and [I].
Call in the window Run with [Win + R],
enter the application identify "cmd" and press Enter
key.
Open the Windows System object in the
Windows Start menu and click on Command Prompt.
This will open a small, ornate window that
will greet you with a brief message and an output like "C:
username;". The latter determines your private listing and cutting-edge
listing on this system. So, when you enter a command, it factors to the
present-day folder besides specifying a directory.
If you now Kind a machine command like
"ping" or "ipconfig", you will get a textual content output
that can be examined in peace. If you allow this kind of command without delay
from Windows by means of Start-Run, the output will solely be seen in a
window for a fraction of a 2nd and then disappear again, because Windows now
routinely closes the vain window.
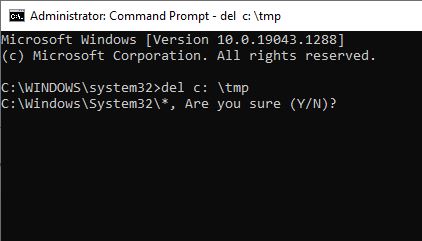
Command-line editions typically have the
gain of being greater efficient. Here's an example: If you favor deleting the
entirety in a particular directory, you can begin Windows Explorer, navigate to
the favored directory, discover all the files, and begin the deletion manner
through the context menu. With the command line, on the different hand, such a
command: del c: \temp
What you Wants, If Yes/No write in Command Prompt.
New facets that come with Windows 10
With the present-day model of Windows,
there are countless new command line strategies:
Mouse wheel with [Ctrl + Shift] adjustments
window clarity.
You can use the Windows Clipboard by way of
mouse and mark with [Ctrl + C] and [Ctrl + V].
[Alt + Return] Changes the command line to
a full display screen mode.
[Ctrl + F] Starts a search window in the
console.
Repeat the final command
DOS veterans comprehend this, attain for
the [F3] key. And this approach nevertheless works to return the remaining
command used at the command on the spot to the Enter line. In the more modern
model of Windows, you can do this with the [up arrow] key. By the way, it works
with different working systems, for instance in the command line of Linux or
Mac OS X.
It is higher to have a listing of the
remaining instructions displayed. To do this, press the [F7] key. You can then
use the cursor key to choose a command and go it to the Enter line.
Unfortunately, instructions are forgotten
as quickly as the Windows command line closes. But for lengthy classes on the
console, this record is very beneficial if you, again and again, want a precise
command.
Use lengthy file names in the command line,
DOS connoisseurs do no longer choose to do besides their command prompt. But
different customers additionally stop up at the magnitude of the occasional
command prompt.
Once you have mastered the frequent
commands, the subsequent hurdle will quickly be waiting: for example, how do
you write a lengthy file identify to replica my Documents My Texts directory?
Solution: Always put a listing identity
with an area in the citation marks, for example, xcopy "My Documents My Texts *
.doc" d:
(This coaching approves you to replica
documents from the named listing to the cutting-edge listing on Force d.)
Quick listing adjustments the usage of tab
keys
Switch to a new listing with the
"CD" command on the command line. Since the introduction of lengthy
file names, it can flip into typing. For example, if you favor going to the
user's non-public area, kind "Marcus"
cd "usersmarkusDokumente"
But in more recent variations of Windows,
the tab key acts as a shortcut. So, you write for example: CD Our [Tab] Mother [Tab] Dock [Tab]
If there are numerous directories for quick
access, such as if the user maria additionally exists in the instance above,
simply press the tab key once more till the favored title appears.
Function key at the command prompt
At the Windows command prompt, these
characteristic keys make it less difficult for you to work with entered
commands:
[F1]: Repeat by way of remaining enter line
character.
[F2]: The before entered command asks which
personality to repeat. (Specific letters are no longer viewed then).
[F3]: Repeats the remaining command-line
completely.
[F4]: asks which persona up to the closing
command ought to be deleted. (Works if you get the command line before entered
with [F8]).
[F5]: History function. A command-line
returns with every keypress. Stop ops in the first command.
[F6]: Sends a Ctrl-Z to the Commands
window. It can be used, for example, to entire the entry of a file with
reproduction con.
[F7]: History function. Shows the most
these days entered instructions in a determination list.
[F8]: History function. Rotating alongside
the command line. The command goes again to the closing command entered after
getting into it first.
[F9]: Shows an enter discipline the place
you can enter the quantity of a command. zero ability the first command
entered.
Environment makes variable entry easier
Windows has a number of hidden surroundings
variables. You can use it as a placeholder for a particular directory.
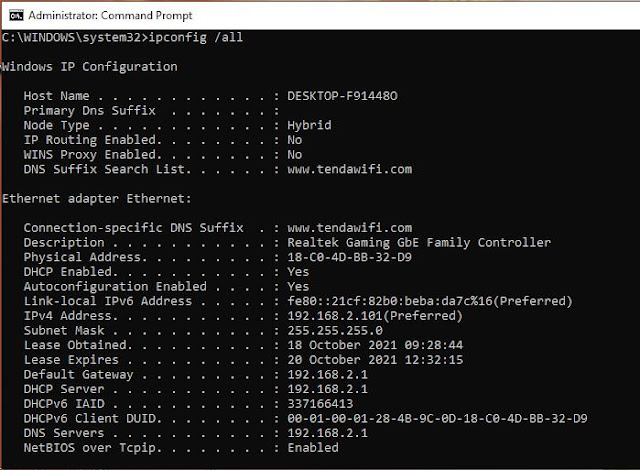
In a regular case, for example, you prefer
the output of a command as a textual content file on the desktop, such as the
output of ipconfig / all for all energetic community connections.
Now you can write about it: ipconfig / all; C: \ Users \ Hanspeter \
Desktop \ netze.txt
Instead, virtually use% homepath%, which
replaces the command line with your non-public person directory. So, you simply
write
ipconfig / all; % homepath% \ Desktop \
netze.txt
Another benefit is that the line produces
correct effects for all personal accounts. So, if you name the command on a
colleague's PC, the file ends up on his laptop except Windows understanding his
username.
Give them a try, it works nicely with asymptomatic echo, such as echo%:
List of beneficial environmental variables
for Windows
% HOMEPATH% - Directory for modern-day user
% WINDIR% - Windows Directory
% SYSTEMDRIVE% - Drive letter for Windows
tough disk
% SESSIONNAME% - Indicates whether or not
the login is a neighborhood ("console) or far off get admission to (eg "
RDP-TCP # 1234 ")
% USERNAME% - Current username
% NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS% - Number of cores
in the CPU
% COMPUTERNAME% - Default PC name
% - contemporary directory
% - cutting-edge date
% TIME% - Current time
% RANDOM% - a random range between zero and
32767
% ERRORLEVEL% - cutting-edge error stage
(for instance after ending some other program)
% CMDCMDLINE% - Calling command-line
interpreter path
% PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE indicates
"x86" for%-32% structures and "AMD64" for 64-bit structures
(including Intel CPUs)
You can honestly output variables by the use
of the Echo command. You can locate the variety of cores in your CPU, for
example, by
Echo% NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS%
Here is the output of a command in Windows
10:
Quick listing modifications the usage of
tab keys
Switch to a new listing with the
"CD" command on the command line. Since the introduction of lengthy
file names, it can flip into typing. For example, if you prefer to go to the
user's non-public area, kind "Marcus"
cd "usersmarkusDokumente"
But in more modern variations of Windows,
the tab key acts as a shortcut. So, you write for example
CD Our [Tab] Mother [Tab] Dock [Tab]
If there are a number of directories for
quick access, such as if the user maria additionally exists in the instance
above, simply press the tab key once more till the preferred identify appears.
Function key at the command prompt
At the Windows command prompt, these
characteristic keys make it less complicated for you to work with entered
commands:
[F1]: Repeat through ultimate enter line
character.
[F2]: The in the past entered command asks
which personality to repeat. (Specific letters are now not considered then).
[F3]: Repeats the remaining command-line
completely.
[F4]: asks which personality up to the
closing command must be deleted. (Works if you get the command line in the past
entered with [F8]).
[F5]: History function. A command-line
returns with every keypress. Stop ops in the first command.
[F6]: Sends a Ctrl-Z to the Commands
window. It can be used, for example, to whole the entry of a file with
reproduction con.
[F7]: History function. Shows the most
these days entered instructions in a determination list.
[F8]: History function. Rotating alongside
the command line. The command goes again to the remaining command entered after
coming into it first.
[F9]: Shows an enter discipline the place
you can enter the wide variety of a command. zero potential the first command
entered.
Environment makes variable entry easier
Windows has a number of hidden surroundings
variables. You can use it as a placeholder for a unique directory.
ipconfig /all; C:\Users\Hanspeter\Desktop\netze.txt
Instead, use the abbreviation% homepath%,
which replaces the command line with your private consumer directory. So, you
simply write
ipconfig / all; % homepath% \ Desktop \
netze.txt
Another benefit is that the line produces
the right end result for all personal accounts. So, if you name the command on a
colleague's PC, the file ends up on his or her laptop except you have to
recognize what his or her username is in Windows.
Try them out, it works fantastic with a
prefixed echo, i.e., echo%:
List of beneficial surroundings
variables in Windows:
% HOMEPATH% - Directory for the
contemporary user
% WINDIR% - Windows directory
% SYSTEMDRIVE% - force letter of the
Windows tough disk
% SESSIONNAME% - Indicates whether or not
login is nearby ("Console) or with the aid of faraway get entry to
(eg" RDP-TCP # 1234 ")
% USERNAME% - contemporary username
% NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS% - wide variety of
cores in the CPU
% COMPUTERNAME% - The assigned identify of
the PC
% - the cutting-edge directory
% - the cutting-edge date
% TIME% - the modern-day time
% RANDOM% - a random quantity between zero
and 32767
% ERRORLEVEL% - modern error stage (for
instance after ending every other program)
% CMDCMDLINE% - Path of the calling command-line interpreter
% PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE% - indicates
"x86" for 32-bit structures and "AMD64" for 64-bit
structures (also with Intel CPUs)
You can truly output the variables by the use
of the echo command. You can discover out the wide variety of cores in your
CPU, for example, by
echo% NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS%
Here is the output of the instructions on a
Windows 10: